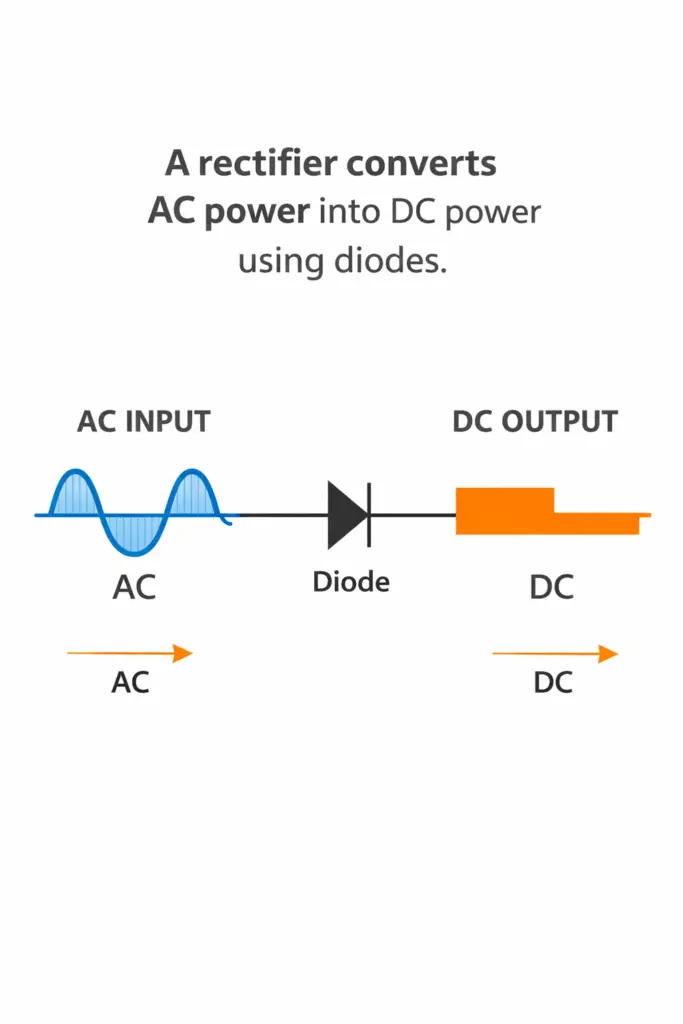
What is a Rectifier?
A rectifier is an electrical circuit that converts AC power into DC power using semiconductor devices called diodes.
A diode allows current to flow in only one direction, which is the basic principle behind rectification.

Basic Working of a Rectifier
When AC voltage is applied to a rectifier circuit:
- The diode conducts current during forward bias
- The diode blocks current during reverse bias
This one-way behavior converts alternating current into unidirectional current.
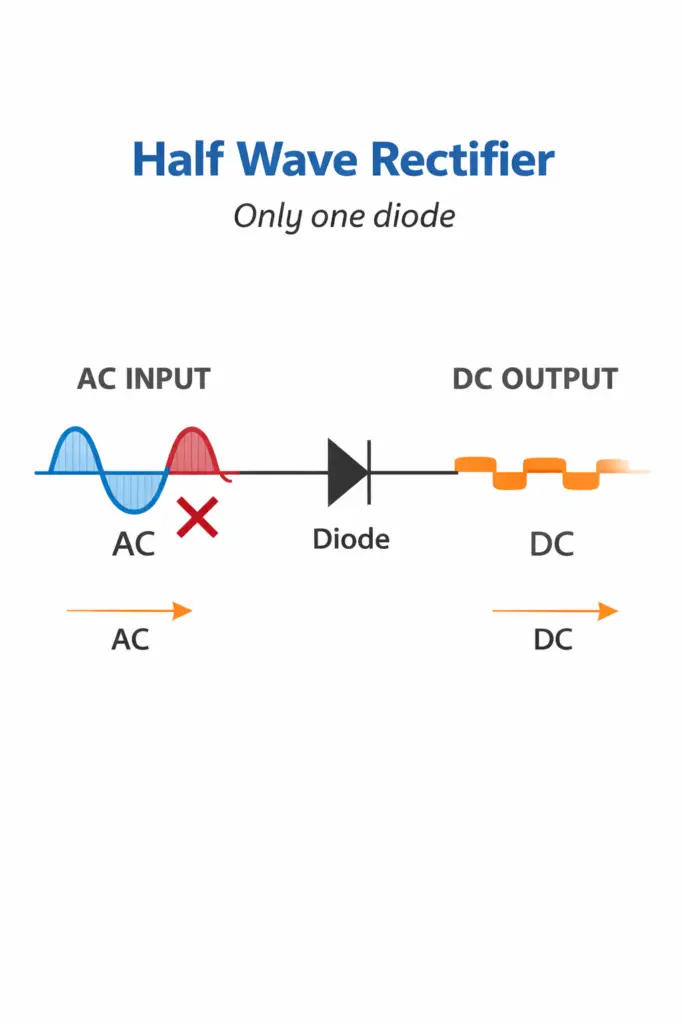
Half Wave Rectifier
A Half Wave Rectifier uses only one diode to convert AC into DC.
Working Principle
- During the positive half cycle of AC input, the diode is forward biased and conducts current.
- During the negative half cycle, the diode is reverse biased and blocks current.
- As a result, only half of the AC waveform appears at the output.
Output Characteristics
- DC output contains large gaps
- High ripple content
- Low efficiency
- Poor voltage regulation
Applications
- Simple demonstration circuits
- Low-power, low-cost applications
- Educational purposes
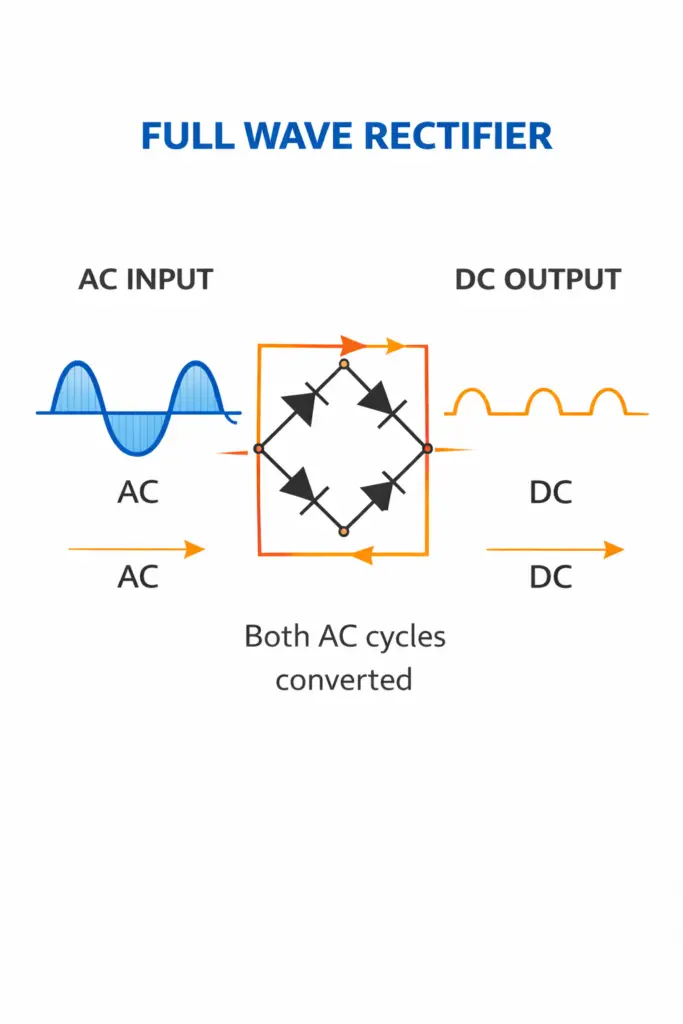
Full Wave Rectifier
A Full Wave Rectifier converts both halves of the AC cycle into DC.
It can be constructed using:
- Two diodes with a center-tapped transformer, or
- Four diodes in a bridge rectifier circuit
Working Principle
- Positive half cycle is converted into DC
- Negative half cycle is also converted into DC
- Output current flows in the same direction for both cycles
Output Characteristics
- Smoother DC output
- Low ripple factor
- High efficiency
- Better voltage regulation
Applications
- Power supply units
- Battery chargers
- DC motor drives
- Electronic and industrial equipment
Half Wave vs Full Wave Rectifier (Comparison)
| Feature | Half Wave Rectifier | Full Wave Rectifier |
|---|---|---|
| Number of diodes | 1 | 2 or 4 |
| AC cycles used | One half | Both halves |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Ripple factor | High | Low |
| DC output | Weak, discontinuous | Smooth, continuous |
| Practical use | Rare | Widely used |
Which Rectifier is Better?
In almost all practical applications, the Full Wave Rectifier is preferred because:
- It provides higher efficiency
- It utilizes the entire AC waveform
- It gives smoother DC output
- It reduces power loss
Half wave rectifiers are mainly used only for learning and basic circuits.
Conclusion
Rectifiers play a critical role in converting AC power into usable DC power.
While Half Wave Rectifiers are simple, they waste half of the input power.
Full Wave Rectifiers, especially bridge rectifiers, are efficient, reliable, and widely used in real-world systems.
