Why ASME Stamps Matter
In industrial fabrication, manufacturing, and repair sectors—especially those dealing with pressure vessels, boilers, and piping systems—compliance isn’t optional. It’s a legal and operational necessity.
One of the most widely accepted ways to prove compliance with safety standards is through ASME Stamps, issued by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). These stamps are not just marks—they’re an assurance that the equipment complies with globally recognized design, fabrication, and inspection requirements.
Let’s dive deep into what each of these stamps means, how they differ, and why they matter.
What Are ASME Stamps?
ASME stamps are certification marks granted to manufacturers or repair organizations that comply with the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC). Each stamp corresponds to a specific code section, reflecting a certain type of pressure-retaining item, its intended use, and level of safety compliance.
From large industrial boilers to miniature pressure vessels, ASME stamps help ensure:
- Consistent manufacturing practices
- Reliable material selection and workmanship
- Code-compliant inspection and testing
- Legal accountability and traceability
Classification of ASME Stamps: Full Overview
Here is a comprehensive breakdown of the various ASME stamps based on their usage, governing code sections, and applications:
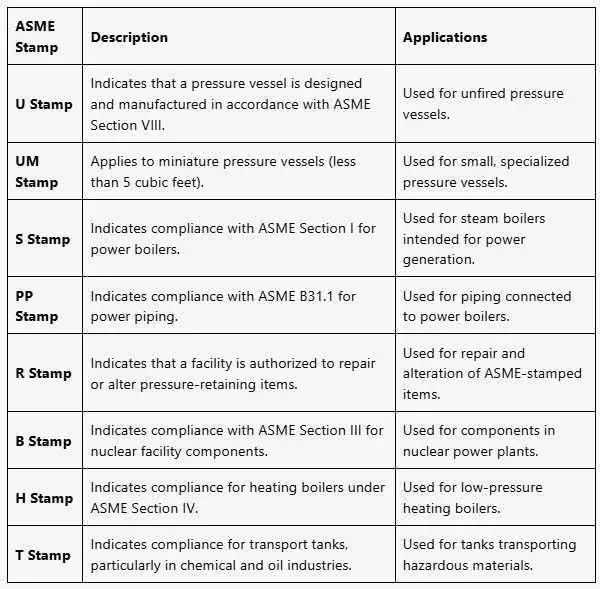
🔧 1. U Stamp
- Code Compliance: ASME Section VIII, Division 1
- Purpose: Certifies that a pressure vessel is designed and manufactured under strict code requirements.
- Applications:
- Unfired pressure vessels such as air receivers, heat exchangers, reactors, separators, and storage tanks.
- Found in petrochemical plants, refineries, and food processing units.
📦 2. UM Stamp
- Code Compliance: ASME Section VIII (Miniature Vessels)
- Purpose: Indicates vessels less than 5 cubic feet are designed and fabricated under the miniature vessel requirements.
- Applications:
- Used for small, specialized vessels like hydraulic accumulators or small air tanks.
♨️ 3. S Stamp
- Code Compliance: ASME Section I
- Purpose: Certifies compliance with design and construction rules for power boilers.
- Applications:
- High-pressure steam boilers used for power generation in thermal plants, refineries, and industrial boilers.
🔄 4. PP Stamp
- Code Compliance: ASME B31.1 – Power Piping Code
- Purpose: Applies to manufacturers of piping systems associated with power boilers.
- Applications:
- Piping connected to power boilers, including steam, feedwater, blowdown, and fuel systems.
🔧 5. R Stamp
- Code Compliance: NBIC (National Board Inspection Code)
- Purpose: Authorizes a facility to repair or alter ASME-certified pressure-retaining items.
- Applications:
- Used in field repairs or shop repairs of pressure vessels, boilers, and piping.
☢️ 6. B Stamp
- Code Compliance: ASME Section III
- Purpose: For nuclear facility components including Class 1, 2, and 3 items.
- Applications:
- Components used in nuclear power plants such as heat exchangers, pumps, and piping.
🔥 7. H Stamp
- Code Compliance: ASME Section IV
- Purpose: Certifies heating boilers for low-pressure applications.
- Applications:
- Residential and commercial heating boilers for hot water or steam service.
🚛 8. T Stamp
- Code Compliance: ASME Section VIII (Transport Vessels)
- Purpose: For transport tanks, particularly in the chemical and petroleum sectors.
- Applications:
- Road or rail tanks for hazardous material transportation like acids, gases, and flammable liquids.
Summary of Differences Between ASME Stamps
📋 Breakdown of Common ASME Stamps
| Stamp | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| U Stamp | Designed and manufactured in accordance with ASME Section VIII | For unfired pressure vessels |
| UM Stamp | For miniature pressure vessels (less than 5 cubic feet) | Specialized, compact vessels |
| S Stamp | Complies with ASME Section I | Steam boilers for power generation |
| PP Stamp | Complies with ASME B31.1 | Power piping connected to boilers |
| R Stamp | Facility authorized to repair/alter ASME-stamped items | Repair and alteration work |
| B Stamp | Complies with ASME Section III | Nuclear facility components |
| H Stamp | Complies with ASME Section IV | Low-pressure heating boilers |
| T Stamp | For transport tanks in chemical/oil industries | Hazardous material tanks |
Why This Knowledge Is Crucial for Fabricators and Operators
Knowing the differences between these stamps isn’t just academic—it affects:
- ✅ Project safety
- ✅ Client trust and approvals
- ✅ Insurance and liability coverage
- ✅ Inspection pass rates
- ✅ Operational uptime
If you’re a fabricator, inspector, or engineer, understanding these distinctions will help you:
- Avoid costly code violations
- Improve project documentation
- Guide procurement and manufacturing decision
Conclusion: A Stamp of Trust and Safety
ASME stamps are more than just a formality—they are a symbol of engineering discipline, quality, and responsibility. Whether you’re dealing with power boilers, chemical tanks, or nuclear facility components, using and recognizing the correct ASME stamp is vital for safe, reliable, and compliant operations.
Stay stamped. Stay safe.
