Welding is a critical process in construction, manufacturing, shipbuilding, pipeline assembly, and many other industries. Ensuring the quality, strength, and safety of a weld joint is paramount. That’s where welding inspection plays a vital role.
A welding inspection checklist helps quality control inspectors, welding engineers, and supervisors ensure that all aspects of the welding process comply with standards such as ASME, AWS, ISO, or company-specific codes.
In this article, we explore the essential checklist items and procedures to be followed before welding, during welding, and after welding for achieving optimal weld quality and preventing costly errors or failures.
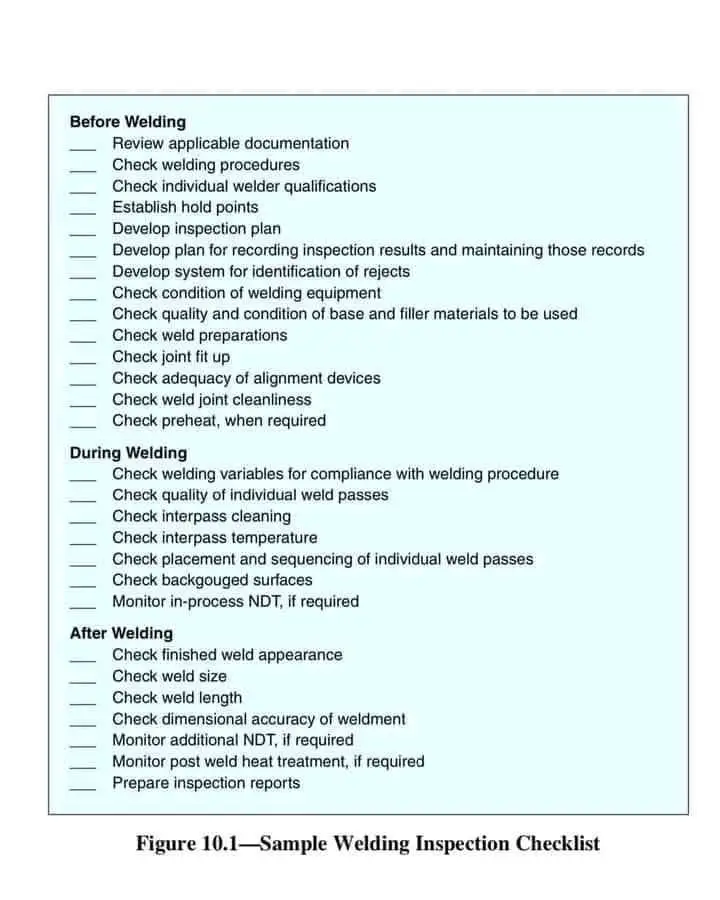
1. Welding Inspection Checklist – Before Welding
✅ 1. Review Applicable Documentation
Inspectors must verify all applicable codes, drawings, specifications, and procedures. Reviewing documentation ensures that the correct welding procedure specifications (WPS), procedure qualification records (PQR), and material test reports (MTRs) are available and applicable to the job.
✅ 2. Check Welding Procedures
Ensure that the WPS is approved and aligns with the required codes. Confirm that it covers the joint design, base and filler materials, welding position, preheat, interpass temperature, and post-weld heat treatment if required.
✅ 3. Check Welder Qualifications
Only qualified welders should perform welding. Verifying welder qualification records as per applicable code (e.g., ASME Section IX or AWS D1.1) ensures they are authorized to weld with specific materials, positions, and techniques.
✅ 4. Establish Hold Points
Hold points are pre-defined stages during fabrication where work is paused for inspection. This ensures that critical operations are verified before progressing.
✅ 5. Develop Inspection Plan
An inspection and test plan (ITP) or quality control plan (QCP) outlines the inspection activities, responsibilities, and acceptance criteria at each stage of welding.
✅ 6. Recordkeeping System
Establish a method for recording inspection results and maintaining records, which is essential for traceability, audits, and certification purposes.
✅ 7. Identification of Rejects
A system should be in place for identifying and tagging rejected items. Marking and isolating defective components prevent them from being used accidentally.
✅ 8. Check Welding Equipment
Inspect the condition of welding machines, torches, cables, and power sources. Faulty equipment can lead to poor weld quality or unsafe operations.
✅ 9. Check Base and Filler Material
Confirm the material specifications (type, grade, size) of base metals and filler metals match the WPS. Also, check storage conditions to prevent contamination.
✅ 10. Weld Preparation
Verify that bevels, groove angles, and surface conditions meet the drawing requirements. Rough or incorrect preparations can lead to weld defects.
✅ 11. Joint Fit-Up
Ensure proper alignment, root gap, and joint setup per WPS or drawings. Poor fit-up may result in dimensional inaccuracy or increased risk of weld defects.
✅ 12. Alignment Devices
Confirm the use and condition of fixtures, jigs, or alignment tools. These devices help maintain correct geometry and positioning during welding.
✅ 13. Joint Cleanliness
Surfaces to be welded must be free from rust, oil, paint, moisture, or any contamination that could compromise weld integrity.
✅ 14. Preheat (if required)
Ensure the correct preheat temperature is achieved and maintained. Preheating reduces the risk of hydrogen-induced cracking, especially in thick or alloy steels.
2. Welding Inspection Checklist – During Welding
✅ 1. Compliance with Welding Parameters
Monitor that the welding parameters (current, voltage, travel speed, heat input) are within WPS limits. Any deviation can lead to unacceptable weld quality.
✅ 2. Check Weld Passes
Inspect each weld pass for defects before proceeding with the next one. Cracks, slag inclusion, or lack of fusion should be corrected immediately.
✅ 3. Interpass Cleaning
Cleaning between weld passes is essential to remove slag or oxides. Poor interpass cleaning can cause defects like lack of fusion or inclusions.
✅ 4. Interpass Temperature
Maintain interpass temperatures as specified. Too high or too low a temperature can alter mechanical properties or cause distortion.
✅ 5. Sequencing of Weld Passes
Monitor the sequence of weld layers and beads. Correct sequencing minimizes residual stresses and distortion, especially in multi-pass welds.
✅ 6. Backgouged Surfaces
Backgouging removes weld metal from the root side of a joint to ensure complete penetration. These surfaces should be inspected for cleanliness and soundness.
✅ 7. In-process NDT (if required)
Sometimes, non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection is required during welding to detect internal flaws in real time.
3. Welding Inspection Checklist – After Welding
✅ 1. Finished Weld Appearance
Inspect the final weld for visual quality — uniform bead appearance, acceptable profile, and absence of cracks, porosity, or undercuts.
✅ 2. Weld Size and Length
Ensure the weld dimensions meet drawing specifications. This includes leg length in fillet welds or throat thickness in groove welds.
✅ 3. Dimensional Accuracy
Measure overall weldment dimensions to ensure they comply with tolerances for squareness, straightness, flatness, etc.
✅ 4. Additional NDT (if required)
Perform final NDT tests like radiography (RT), ultrasonic testing (UT), or dye penetrant testing (PT) to ensure the internal integrity of the weld.
✅ 5. Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT)
If specified, monitor the PWHT process, which relieves residual stresses and restores desired mechanical properties in certain materials.
✅ 6. Prepare Inspection Reports
Compile all results, including visual, dimensional, and NDT inspection findings. Documentation is crucial for quality records, client submission, and regulatory compliance.
Why Use a Welding Inspection Checklist?
Using a formal checklist ensures:
- Compliance with codes and client specifications
- Consistency across multiple projects or welders
- Early detection of potential issues
- Improved safety and structural integrity
- Reduced rework, delays, and associated costs
- Traceability and accountability through records
Final Thoughts
Welding is not just about melting metals together — it’s a precise process that demands quality at every stage. An effective welding inspection checklist before, during, and after welding serves as a roadmap for maintaining high standards, reducing defects, and ensuring the durability of the final product.
Whether you’re a welding inspector, quality engineer, or a welder aiming for excellence, adopting such systematic inspection practices can make a significant difference in project success and safety.

Welding inspection training
I need welding inspection training